===
Index
二叉树遍历
先序遍历
递归写法:
vector<int> res;
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (root) {
res.push_back(root->val);
preorderTraversal(root->left);
preorderTraversal(root->right);
}
}
非递归写法:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
stack<TreeNode*> stk;
TreeNode* p = root;
while (p || !stk.empty()) {
while (p) {
res.push_back(p->val);
stk.push(p);
p = p->left;
}
if (!stk.empty()) {
p = stk.top();
stk.pop();
p = p->right;
}
}
return res;
}
中序遍历
递归写法:
vector<int> res;
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (root) {
preorderTraversal(root->left);
res.push_back(root->val);
preorderTraversal(root->right);
}
}
非递归写法:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
stack<TreeNode*> stk;
TreeNode* p = root;
while (p || !stk.empty()) {
while (p) {
stk.push(p);
p = p->left;
}
if (!stk.empty()) {
p = stk.top();
res.push_back(p->val);
stk.pop();
p = p->right;
}
}
return res;
}
后序遍历
递归写法:
vector<int> res;
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (root) {
preorderTraversal(root->left);
preorderTraversal(root->right);
res.push_back(root->val);
}
}
非递归写法:
- pre: root, left, right
- post: left, right, root
- root->left->right -> root->right->left -> left->right->root
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
stack<TreeNode*> stk;
TreeNode* p = root;
while (p || !stk.empty()) {
while (p) {
stk.push(p);
res.push_back(p->val);
p = p->right;
}
if (!stk.empty()) {
p = stk.top();
stk.pop();
p = p->left;
}
}
return vector<int>(res.rbegin(), res.rend());
}
二叉树的层次遍历ii
vector<vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return {};
vector<vector<int>> res;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
int sz = q.size();
vector<int> v(sz);
for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++i) {
TreeNode* tmp = q.front();
q.pop();
v[i] = tmp->val;
if (tmp->left) q.push(tmp->left);
if (tmp->right) q.push(tmp->right);
}
res.push_back(v);
}
reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
return res;
}
二叉树的锯齿形层次遍历
vector<vector<int>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return {};
vector<vector<int>> ans;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
bool rev = false;
while (!q.empty()) {
int sz = q.size();
vector<int> tmp(sz);
for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++i) {
auto p = q.front();
q.pop();
if (rev) tmp[sz - 1 - i] = p->val;
else tmp[i] = p->val;
if (p->left) q.push(p->left);
if (p->right) q.push(p->right);
}
ans.push_back(tmp);
rev = !rev;
}
return ans;
}
n叉树的层序遍历
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
if(!root) return res;
queue<Node*> que;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()){
int size=que.size();
vector<int> tmp;
while(size--){
Node *p=que.front();
que.pop();
tmp.push_back(p->val);
for(int i=0;i<p->children.size();i++)
que.push(p->children[i]);
}
res.push_back(tmp);
}
return res;
}
二叉树的垂直遍历
给你一个二叉树的根结点,返回其结点按 垂直方向(从上到下,逐列)遍历的结果。 如果两个结点在同一行和列,那么顺序则为 从左到右。(leetcode 314)
示例
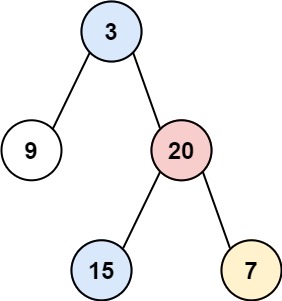
- 输入: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
- 输出: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]]
分析
- 用节点的x坐标来分类左右,root x坐标为0,其left为-1,right为1.
- 使用map存储每个x坐标的元素集合,map会自动按照x坐标排序
vector<vector<int>> verticalOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return {};
map<int, vector<int>> mp;
queue<pair<TreeNode*, int>> q;
q.push({root, 0});
while (!q.empty()) {
auto [p, x] = q.front();
q.pop();
mp[x].push_back(p->val);
if (p->left) q.push({p->left, x - 1});
if (p->right) q.push({p->right, x + 1});
}
vector<vector<int>> res;
for (auto [x, v] : mp) res.push_back(v);
return res;
}
二叉树构造
从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& pre, vector<int>& in) {
return build(pre, 0, pre.size(), in, 0, in.size());
}
TreeNode* build(vector<int>& pre, int sp, int ep, vector<int>& in, int si, int ei) {
if (sp == ep) return NULL;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(pre[sp]);
int dis = find(in.begin() + si, in.begin() + ei, pre[sp]) - in.begin() - si;
root->left = build(pre, sp + 1, sp + 1 + dis, in, si, si + dis);
root->right = build(pre, sp + 1 + dis, ep, in, si + dis + 1, ei);
return root;
}
从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
TreeNode* build(vector<int>& in, vector<int>& post, int lin, int lpo, int len){
if(len == 0) return NULL;
TreeNode * root = new TreeNode(post[lpo + len-1]);
int pos = 0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(in[i+lin] == root->val){
pos = i;
break;
}
}
root->left = build(in,post,lin,lpo,pos);
root->right = build(in,post,lin+pos+1,lpo+pos,len-pos-1);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
return build(inorder, postorder,0,0,inorder.size());
}
恢复二叉搜索树
给你二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,该树中的两个节点被错误地交换。请在不改变其结构的情况下,恢复这棵树。
class Solution {
TreeNode *p1 {NULL}, *p2 {NULL}, *pre {NULL};
public:
void recoverTree(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
swap(p1->val, p2->val);
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return;
dfs(root->left);
if(!p1 && pre && pre->val >= root->val) p1 = pre;
if(p1 && pre && pre->val >= root->val) p2 = root;
pre = root;
dfs(root->right);
}
};
填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
给定一个完美二叉树,其所有叶子节点都在同一层,每个父节点都有两个子节点。二叉树定义如下:
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
递归方法:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
if (!root) return NULL;
if (root->left) {
root->left->next = root->right;
if (root->next) root->right->next = root->next->left;
connect(root->left);
connect(root->right);
}
return root;
}
非递归写法:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
Node *pre = root, *cur;
while (pre) {
cur = pre;
while (cur && cur->left) {
cur->left->next = cur->right;
if (cur->next) cur->right->next = cur->next->left;
cur = cur->next;
}
pre = pre->left;
}
return root;
}
填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针2
Node* connect(Node* root) {
dfs(root);
return root;
}
void dfs(Node *root) {
if (!root) return;
Node dummy(INT_MIN);
for (auto cur = root, pre = &dummy; cur; cur = cur->next) {
if (cur->left) {
pre->next = cur->left;
pre = pre->next;
}
if (cur->right) {
pre->next = cur->right;
pre = pre->next;
}
}
dfs(dummy.next);
}
最大二叉树
给定一个不含重复元素的整数数组 nums 。一个以此数组直接递归构建的 最大二叉树 定义如下:
- 二叉树的根是数组 nums 中的最大元素。
- 左子树是通过数组中 最大值左边部分 递归构造出的最大二叉树。
- 右子树是通过数组中 最大值右边部分 递归构造出的最大二叉树。
返回有给定数组 nums 构建的 最大二叉树 。
using iter = vector<int>::iterator;
TreeNode* dfs(iter l, iter r) {
if (l == r) return nullptr;
auto it = max_element(l, r);
auto tn = new TreeNode(*it);
tn->left = dfs(l, it);
tn->right = dfs(it + 1, r);
return tn;
}
TreeNode* constructMaximumBinaryTree(vector<int>& nums) {
return dfs(nums.begin(), nums.end());
}
最大二叉树2
最大树定义:一个树,其中每个节点的值都大于其子树中的任何其他值。
向最大树root中添加一值为val的节点,如果val大于root的值,那么就把root当做值为val节点左孩子,否则,就把val插入到右孩子的相应位置。
TreeNode* insertIntoMaxTree(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if (!root) return new TreeNode(val);
if (root->val < val) {
auto p = new TreeNode(val);
p->left = root;
return p;
} else {
root->right = insertIntoMaxTree(root->right, val);
return root;
}
return nullptr;
}
二叉树查找
二叉搜索树中第k小的元素
给定一个二叉搜索树,编写一个函数 kthSmallest 来查找其中第 k 个最小的元素。
说明: 你可以假设 k 总是有效的,1 ≤ k ≤ 二叉搜索树元素个数。
int kthSmallest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
stack<TreeNode *> st;
TreeNode *p = root;
while (p || !st.empty()) {
while (p) {
st.push(p);
p = p->left;
}
p = st.top();
if(--k == 0) return p->val;
st.pop();
p = p->right;
}
return 0;
}
二叉搜索树的中序后继
给定一个二叉查找树,以及一个节点,求该节点在中序遍历的后继,如果没有则返回null
讲解 中序遍历的后继:
- 如果该节点有右子节点,那么后继是其右子节点子树中最左端的节点。
- 如果该节点无右子节点,那么后继是离它最近的祖先,该节点在这个祖先的左子树内
1.递归
TreeNode * inorderSuccessor(TreeNode * root, TreeNode * p) {
if (!root) return root;
if (root->val <= p->val)
return inorderSuccessor(root->right, p);
auto left = inorderSuccessor(root->left, p);
return left ? left : root;
}
2.循环
- 查找该节点,并在该过程中维护上述性质的祖先节点
- 查找到后,如果该节点有右子节点,则后继在其右子树内,否则后继就是维护的那个祖先节点。
TreeNode * inorderSuccessor(TreeNode * root, TreeNode * p) {
TreeNode* fa = nullptr;
while (root && root != p) {
if (root->val < p->val)
root = root->right;
else {
fa = root;
root = root->left;
}
}
if (!root) return nullptr;
if (!root->right) return fa;
root = root->right;
while (root->left)
root = root->left;
return root;
}
二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if (!root) return root;
if(root->val > p->val && root->val > q->val)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
if (root->val < p->val && root->val < q->val)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
return root;
}
二叉树的最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if (!root || root == p || root == q) return root;
auto l = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q),
auto r = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if (!r) return l;
if (!l) return r;
return root;
}
二叉树的下一个节点
给定一个二叉树和其中的一个结点,请找出中序遍历顺序的下一个结点并且返回。注意,树中的结点不仅包含左右子结点,同时包含指向父结点的指针。
struct TreeLinkNode {
int val;
struct TreeLinkNode *left;
struct TreeLinkNode *right;
struct TreeLinkNode *next;
TreeLinkNode(int x) :val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {}
};
思路
- 如果一个节点的右子树不为空,那么下一个节点是该右子树的最左叶子
- 否则(右子树为空),沿父节点向上直到找到某个节点是其父节点的左孩子,那么该父节点就是下一个节点
TreeLinkNode* GetNext(TreeLinkNode* pNode) {
if (!pNode) return nullptr;
if (pNode->right) {
auto p = pNode->right;
while (p->left) p = p->left;
return p;
} else {
auto p = pNode;
while (p->next) {
if (p->next->left == p) return p->next;
p = p->next;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
二叉树转换
二叉树的序列化与反序列化
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return "#";
return to_string(root->val) + "," + serialize(root->left) + "," + serialize(root->right);
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
if (data == "#") return NULL;
stringstream s(data);
return deserialize(s);
}
TreeNode* deserialize(stringstream& s) {
string str;
getline(s, str, ',');
if (str == "#") return NULL;
else {
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(stoi(str));
root->left = deserialize(s);
root->right = deserialize(s);
return root;
}
}
二叉树展开为链表
给定一个二叉树,原地将它展开为一个单链表。
例如,给定二叉树:
1
/ \
2 5
/ \ \
3 4 6
将其展开为:
1 —— 2 —— 3 —— 4 —— 5 —— 6
递归解法:
TreeNode* last = nullptr;
void flatten(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return;
flatten(root->right);
flatten(root->left);
root->right = last;
root->left = nullptr;
last = root;
}
非递归解法:
void flatten(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return;
TreeNode *left = nullptr;
while (root) {
left = root->left;
if (left) {
while (left->right) left = left->right;
left->right = root->right;
root->right = root->left;
root->left = nullptr;
}
root = root->right;
}
}
把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
给定一个二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree),把它转换成为累加树(Greater Tree),使得每个节点的值是原来的节点值加上所有大于它的节点值之和。
int sum = 0;
TreeNode* convertBST(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return root;
convertBST(root->right);
root->val += sum;
sum = root->val;
convertBST(root->left);
return root;
}
翻转二叉树
将一颗二叉树翻转为其镜像二叉树
递归方法
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return root;
auto t = invertTree(root->left);
root->left = invertTree(root->right);
root->right = t;
return root;
}
非递归解法
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return root;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
auto p = q.front();
q.pop();
auto left = p->left;
p->left = p->right;
p->right = left;
if (p->left) q.push(p->left);
if (p->right) q.push(p->right);
}
return root;
}
上下翻转二叉树
给定一个二叉树,其中所有的右节点要么是具有兄弟节点(拥有相同父节点的左节点)的叶节点,要么为空,将此二叉树上下翻转并将它变成一棵树, 原来的右节点将转换成左叶节点。返回新的根。
示例
输入: 1
2 3
4 5
输出: 4
5 2
3 1
递归法
TreeNode* upsideDownBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root || !root->left) return root;
auto left = root->left, right = root->right;
auto lv = upsideDownBinaryTree(left);
left->left = right;
left->right = root;
root->left = root->right = nullptr;
return lv;
}
迭代法
TreeNode* upsideDownBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
auto cur = root;
TreeNode *pre = nullptr, *tmp = nullptr;
while (cur) {
auto next = cur->left;
cur->left = tmp; // copy original right to left
tmp = cur->right; // save next level original right
cur->right = pre; // copy original root to right
pre = cur; // save cur root, i.e: next level left
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
子树
寻找重复的子树
给定一棵二叉树,返回所有重复的子树。对于同一类的重复子树,你只需要返回其中任意一棵的根结点即可。
两棵树重复是指它们具有相同的结构以及相同的结点值。
unordered_map<string, int> mp;
vector<TreeNode*> res;
vector<TreeNode*> findDuplicateSubtrees(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
return res;
}
string dfs(TreeNode *root) {
if (!root) return "";
auto s = to_string(root->val) + "," + dfs(root->left) + "," + dfs(root->right);
if (mp[s]++ == 1) res.push_back(root);
return s;
}
另一个树的子树
给定两个非空二叉树 s 和 t,检验 s 中是否包含和 t 具有相同结构和节点值的子树。s 的一个子树包括 s 的一个节点和这个节点的所有子孙。s 也可以看做它自身的一棵子树。
bool isSame(TreeNode* s, TreeNode* t) {
if (!s || !t) return s == t;
return (s->val == t->val && isSame(s->left, t->left) && isSame(s->right, t->right));
}
bool isSubtree(TreeNode* s, TreeNode* t) {
if (!s || !t) return t == nullptr;
return isSame(s, t) || isSubtree(s->left, t) || isSubtree(s->right, t);
}
二叉树路径
路径总和2
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,找到所有从根节点到叶子节点路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
void rec(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
if (!root) return;
path.push_back(root->val);
if (!root->left && !root->right && root->val == sum) res.push_back(path);
rec(root->left, sum - root->val);
rec(root->right, sum - root->val);
path.pop_back();
}
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
rec(root, sum);
return res;
}
路径总和3
给定一个二叉树,它的每个结点都存放着一个整数值。
找出路径和等于给定数值的路径总数。
路径不需要从根节点开始,也不需要在叶子节点结束,但是路径方向必须是向下的(只能从父节点到子节点)。
二叉树不超过1000个节点,且节点数值范围是 [-1000000,1000000] 的整数。
int pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
unordered_map<int, int> cnt0;
return dfs(root, sum, cnt, 0);
}
int dfs(TreeNode* root, int sum, unordered_map<int, int> &cnt, int pre) {
if (!root) return 0;
pre += root->val;
int ans = cnt[pre - sum];
++cnt[pre];
ans += dfs(root->left, sum, cnt, pre) + dfs(root->right, sum, cnt, pre);
--cnt[pre];
return ans;
}
二叉树的最大路径和
路径 被定义为一条从树中任意节点出发,沿父节点-子节点连接,达到任意节点的序列。同一个节点在一条路径序列中 至多出现一次 。该路径 至少包含一个 节点,且不一定经过根节点。
路径和 是路径中各节点值的总和。
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其 最大路径和 。
int ans = INT_MIN;
int dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
int l = max(0, dfs(root->left)), r = max(0, dfs(root->right));
ans = max(ans, root->val + l + r);
return max(l, r) + root->val;
}
int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
二叉树的所有路径
给定一个二叉树,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
vector<string> res;
void dfs(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& path) {
path.push_back(root->val);
if (!root->left && !root->right) {
string str;
for (int i = 0; i < path.size(); ++i) {
if (i) str += "->" + to_string(path[i]);
else str += to_string(path[i]);
}
res.push_back(str);
return;
}
if (root->left) {
dfs(root->left, path);
path.pop_back();
}
if (root->right) {
dfs(root->right, path);
path.pop_back();
}
}
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return {};
vector<int> path;
dfs(root, path);
return res;
}
二叉树中的最长交错路径
给你一棵以 root 为根的二叉树,二叉树中的交错路径定义如下:
- 选择二叉树中 任意 节点和一个方向(左或者右)。
- 如果前进方向为右,那么移动到当前节点的的右子节点,否则移动到它的左子节点。
- 改变前进方向:左变右或者右变左。
- 重复第二步和第三步,直到你在树中无法继续移动。
- 交错路径的长度定义为:访问过的节点数目 - 1(单个节点的路径长度为 0 )。
请你返回给定树中最长 交错路径 的长度。
int ans = 0;
void dfs(TreeNode* o, bool dir, int len) {
ans = max(ans, len);
if (!dir) {
if (o->left) dfs(o->left, 1, len + 1);
if (o->right) dfs(o->right, 0, 1);
} else {
if (o->right) dfs(o->right, 0, len + 1);
if (o->left) dfs(o->left, 1, 1);
}
}
int longestZigZag(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
dfs(root, 0, 0); // 0 => left
dfs(root, 1, 0); // 1 => right
return ans;
}
二叉树的直径
给定一颗二叉树,您需要计算树的直径长度。 二叉树的直径是树中任意两个节点之间最长路径的长度。
int ans = 0;
int dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
int left = dfs(root->left);
int right = dfs(root->right);
ans = max(ans, left + right);
return max(left, right) + 1;
}
int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode * root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
其它
分裂二叉树的最大乘积
给你一棵二叉树,它的根为 root 。请你删除 1 条边,使二叉树分裂成两棵子树,且它们子树和的乘积尽可能大。
由于答案可能会很大,请你将结果对 10^9 + 7 取模后再返回。
int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
long long sum = 0, ret = 0; //节点和为sum,则每棵子树和尽量接近sum/2时,乘积最大。
int subsum(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
long long s = subsum(root->left) + subsum(root->right) + root->val;
if (abs(sum - 2 * s) < abs(sum - 2 * ret)) ret = s;
return s;
}
int maxProduct(TreeNode* root) {
sum = subsum(root);
subsum(root);
return ret * (sum - ret) % MOD;
}
二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历结果。如果是则返回 true,否则返回 false。假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同。
1.单调栈解法 后序遍历: 左、右、根 后序遍历的逆序: 根、右、左
往右子树遍历的过程,value是越来越大的,一旦出现了value小于栈顶元素value的时候,就表示要开始进入左子树了(如果不是,就应该继续进入右子树,否则不满足二叉搜索树的定义,不理解的请看下二叉搜索树的定义),但是这个左子树是从哪个节点开始的呢?
单调栈帮我们记录了这些节点,只要栈顶元素还比当前节点大,就表示还是右子树,要移除,因为我们要找到这个左孩子节点直接连接的父节点,也就是找到这个子树的根,只要栈顶元素还大于当前节点,就要一直弹出,直到栈顶元素小于节点,或者栈为空。栈顶的上一个元素就是子树节点的根。
接下来,数组继续往前遍历,之后的左子树的每个节点,都要比子树的根要小,才能满足二叉搜索树,否则就不是二叉搜索树。
bool verifyPostorder(vector<int>& po) {
stack<int> stk;
int root = INT_MAX;
for(int i = po.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if(po[i] > root) return false;
while(!stk.empty() && stk.top() > po[i]) {
root = stk.top();
stk.pop();
}
stk.push(po[i]);
}
return true;
}
2.递归解法
bool dfs(vector<int>& po, int s, int e) {
if (s >= e) return true;
int p = s, v = po[e];
while (po[p] < v) ++p;
int l = p - 1;
while (po[p] > v) ++p;
return p == e && dfs(po, s, l) && dfs(po, l+1,e-1);
}
bool verifyPostorder(vector<int>& po) {
return dfs(po, 0, po.size()-1);
}
二叉树最大宽度
给定一个二叉树,编写一个函数来获取这个树的最大宽度。树的宽度是所有层中的最大宽度。这个二叉树与满二叉树(full binary tree)结构相同,但一些节点为空。
每一层的宽度被定义为两个端点(该层最左和最右的非空节点,两端点间的null节点也计入长度)之间的长度。
using P = pair<TreeNode*, int>;
int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
queue<P> q;
q.push({root ,1});
int res = 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
int sz = q.size(), l = q.front().second, r;
for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++i) {
auto v = q.front();
q.pop();
auto t = v.first;
int p = v.second - l + 1;
r = v.second;
if (t->left) q.push({t->left, p * 2});
if (t->right) q.push({t->right, p * 2 + 1});
}
res = max(res, r - l + 1);
}
return res;
}
二叉树的右视图
void dfs(TreeNode * root, int lv, vector<int>& res) {
if (!root) return;
if (lv >= res.size()) res.push_back(root->val);
dfs (root->right, lv + 1, res);
dfs (root->left, lv + 1, res);
}
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
dfs(root, 0, res);
return res;
}
二叉树的边界
二叉树的 边界 是由 根节点 、左边界 、按从左到右顺序的 叶节点 和 逆序的右边界 ,按顺序依次连接组成。
vector<int> res;
void dfs(TreeNode* root, bool lbound, bool rbound) {
if (!root) return;
if (lbound) res.push_back(root->val);
else if (!root->left && !root->right) {
res.push_back(root->val);
return;
}
dfs(root->left, lbound, !lbound && rbound && !root->right);
dfs(root->right, !rbound && lbound && !root->left, rbound);
if (!lbound && rbound) res.push_back(root->val);
}
vector<int> boundaryOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root, true, true);
return res;
}





