===
Index
用两个栈模拟队列
用两个栈来实现一个队列,完成队列的 Push 和 Pop 操作。
思路
- 假设 stack_in 用于处理入栈操作,stack_out用于处理出栈操作
- stack_in 按栈的方式正常处理入栈数据;
- 关键在于出栈操作 当stack_out为空时,需要先将每个stack_in中的数据出栈后压入stack_out 反之,每次弹出stack_out栈顶元素即可
class Solution {
stack<int> stack_in;
stack<int> stack_out;
public:
void push(int node) {
stack_in.push(node);
}
int pop() {
if(stack_out.size() <= 0) {
while (stack_in.size() > 0) {
auto tmp = stack_in.top();
stack_in.pop();
stack_out.push(tmp);
}
}
auto ret = stack_out.top();
stack_out.pop();
return ret;
}
};
最小栈
设计一个支持 push ,pop ,top 操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
- push(x) —— 将元素 x 推入栈中。
- pop() —— 删除栈顶的元素。
- top() —— 获取栈顶元素。
- getMin() —— 检索栈中的最小元素。
只用一个栈的方法:
class MinStack {
stack<int> a;
int min;
public:
MinStack():min(INT_MAX){}
void push(int x) {
if(x <= min) {
a.push(min); min = x;
}
a.push(x);
}
void pop() {
int t = a.top(); a.pop();
if (t == min) {
min = a.top(); a.pop();
}
}
int top() {
return a.top();
}
int getMin() {
return min;
}
};
使用两个栈:
class MinStack {
private:
stack<pair<int, int> > stk;
int min;
public:
/** initialize your data structure here. */
MinStack() {
min = INT_MAX;
}
void push(int x) {
if(x < min) min = x;
stk.push(pair<int,int>(min,x));
}
void pop() {
stk.pop();
if(stk.empty()){
min = INT_MAX;
}else{
min = stk.top().first;
}
}
int top() {
return stk.top().second;
}
int getMin() {
return stk.top().first;
}
};
lru缓存机制
运用你所掌握的数据结构,设计和实现一个 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存机制。它应该支持以下操作: 获取数据 get 和 写入数据 put 。
- 获取数据 get(key) - 如果关键字 (key) 存在于缓存中,则获取关键字的值(总是正数),否则返回 -1。
- 写入数据 put(key, value) - 如果关键字已经存在,则变更其数据值;如果关键字不存在,则插入该组「关键字/值」。当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最久未使用的数据值,从而为新的数据值留出空间。
进阶: 你是否可以在 O(1) 时间复杂度内完成这两种操作?
class LRUCache {
struct Node {
int k, v;
Node(int _k, int _v): k(_k), v(_v) {}
};
int cap;
list<Node> ls;
unordered_map<int, list<Node>::iterator> um;
public:
LRUCache(int capacity) :cap(capacity){}
int get(int key) {
if (um.find(key) == um.end()) return -1;
ls.splice(ls.begin(), ls, um[key]);
return um[key]->v;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
if (get(key) != -1) {
um[key]->v = value;
return;
}
if (um.size() == cap) {
um.erase(ls.back().k);
ls.pop_back();
}
ls.emplace_front(key, value);
um[key] = ls.begin();
}
};
lfu缓存
请你为 最不经常使用(LFU)缓存算法设计并实现数据结构。
实现 LFUCache 类:
- LFUCache(int capacity) - 用数据结构的容量 capacity 初始化对象
- int get(int key) - 如果键存在于缓存中,则获取键的值,否则返回 -1。
- void put(int key, int value) - 如果键已存在,则变更其值;如果键不存在,请插入键值对。当缓存达到其容量时,则应该在插入新项之前,使最不经常使用的项无效。在此问题中,当存在平局(即两个或更多个键具有相同使用频率)时,应该去除 最久未使用 的键。 注意「项的使用次数」就是自插入该项以来对其调用 get 和 put 函数的次数之和。使用次数会在对应项被移除后置为 0 。
为了确定最不常使用的键,可以为缓存中的每个键维护一个 使用计数器 。使用计数最小的键是最久未使用的键。
当一个键首次插入到缓存中时,它的使用计数器被设置为 1 (由于 put 操作)。对缓存中的键执行 get 或 put 操作,使用计数器的值将会递增。
class LFUCache {
int capacity, min_freq;
unordered_map<int, pair<int, int>> kv_freq;
unordered_map<int, list<int>> freq_k;
unordered_map<int, list<int>::iterator> k_iter;
public:
LFUCache(int capacity) : capacity(capacity) {}
int get(int key) {
if (kv_freq.find(key) == kv_freq.end()) return -1;
int freq = kv_freq[key].second;
freq_k[freq++].erase(k_iter[key]);
freq_k[freq].emplace_front(key);
k_iter[key] = freq_k[freq].begin();
kv_freq[key].second = freq;
if (freq_k[min_freq].empty()) min_freq = freq;
return kv_freq[key].first;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
if (capacity <= 0) return;
if (get(key) != -1) {
kv_freq[key].first = value;
return;
}
if (kv_freq.size() == capacity) {
int del_k = freq_k[min_freq].back();
freq_k[min_freq].pop_back();
kv_freq.erase(del_k);
k_iter.erase(del_k);
}
min_freq = 1;
kv_freq[key] = {value, min_freq};
freq_k[min_freq].emplace_front(key);
k_iter[key] = freq_k[min_freq].begin();
}
};
添加与搜索单词
请你设计一个数据结构,支持 添加新单词 和 查找字符串是否与任何先前添加的字符串匹配 。
实现字典类 WordDictionary
WordDictionary()初始化词典对象void addWord()将word添加到数据结构中,之后可以对它进行匹配bool search(word)如果数据结构中存在字符串与word匹配,则返回true,否则返回false。word中可能包含一些 ‘.’ ,每个’.’都可以匹配任何一个字母。
struct TrieNode{
TrieNode* children[26];
bool isWord;
TrieNode():isWord(false) {
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) children[i] = nullptr;
}
};
class WordDictionary {
TrieNode* root = new TrieNode();
public:
WordDictionary() {}
void addWord(string word) {
TrieNode* node = root;
for(auto ch : word) {
if (node->children[ch - 'a'] == nullptr)
node->children[ch - 'a'] = new TrieNode();
node = node->children[ch - 'a'];
}
node->isWord = true;
}
bool search(string word) {
return dfs(0, word, root);
}
bool dfs(int idx, string word, TrieNode* root) {
if (idx == word.size()) return root->isWord;
if (word[idx] != '.')
return root->children[word[idx] - 'a'] && dfs(idx + 1, word, root->children[word[idx] - 'a']);
else {
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) {
if (root->children[i]) {
if (dfs(idx + 1, word, root->children[i])) return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
};
树状数组
简介
- 树状数组是一种用于维护前缀信息的数据结构
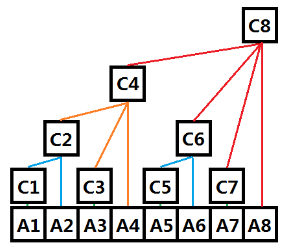
- 树状数组
C在物理空间上是连续的; - 对于数组中的两个位置
C[x], C[y],若满足y = x + 2^k(其中k表示x二进制中末尾 0 的个数),则定义C[x], C[y]为一组父子关系;4 的二进制为 100,则 k = 2 所以 4 是 4 + 2^2 = 8 的孩子 5 的二进制位 101,则 k = 0 所以 5 是 5 + 2^0 = 6 的孩子 - 由以上定义,可知奇数下标的位置一定是叶子节点
C[i] 的直观含义
C[i]实际上表示原数组中一段区间内的某个统计意义(区间和、区间积、区间最值等等);- 该区间为
[i-2^k+1, i],是一个闭区间; - 以区间和为例
1=(001) C[1]=A[1]; 2=(010) C[2]=A[1]+A[2]; 3=(011) C[3]=A[3]; 4=(100) C[4]=A[1]+A[2]+A[3]+A[4]; 5=(101) C[5]=A[5]; 6=(110) C[6]=A[5]+A[6]; 7=(111) C[7]=A[7]; 8=(1000) C[8]=A[1]+A[2]+A[3]+A[4]+A[5]+A[6]+A[7]+A[8];
树状数组解决的几个问题
//初始化
void build(vector<int> &nums) {
n = nums.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
add(i + 1, nums[i]);
}
void add(int x, int k) {
for (; x <= n; x += lowbit(x))
tr[x] += k;
}
int query(int x) {
int ans = 0;
for (; x; x -= lowbit(x))
ans += tr[x];
return ans;
}
单点修改,单点查询
add(x, k)
query(x) - query(x - 1)
单点修改,区间查询
add(x, k)
query(r) - query(l - 1) // [l, r]的和 数组下标从1开始
区间修改,单点查询
add(l, d); add(r + 1, -d);
a[x] + query(x) //查询a[x]
区间修改,区间查询
int t1[maxn], t2[maxn];
void add1(int x, int k) {
for (; x <= n; x += lowbit(x)) t1[x] += k;
}
int query1(int x) {
int ans = 0;
for (; x; x -= lowbit(x)) ans += t1[x];
return ans;
}
void add2(int x, int k) {
for (; x <= n; x += lowbit(x)) t2[x] += k;
}
int query2(int x) {
int ans = 0;
for (; x; x -= lowbit(x)) ans += t2[x];
return ans;
}
//区间修改操作 [l,r] 区间每个数+d
add1(l, d); add1(r + 1, -d);
add2(l, l * d), add2(r + 1, -(r + 1) * d);
//区间查询 [l, r]的和
(sum[r] + (r+1)*query1(r) - query2(r)) - (sum[l - 1] + l * query1(l-1) - query2(l - 1));
树状数组的特点
- 线段树不能解决的问题,树状数组也无法解决;
- 树状数组和线段树的时间复杂度相同:初始化
O(n),查询和修改O(logn);但实际效率要高于线段树; - 直接维护前缀信息也能解决查询问题,但是修改的时间复杂度会比较高;
一维树状数组
用法
- 初始化: FenwickTree
fen(n); 或者 FenwickTree fen(a); a 是 vector - 添加元素: fen.add(i, val) 0 <= i < n;
- 查询前缀和: fen.ask(i) 0 <= i < n
- 查询区间和: fen.ask(x, y) a[x] + …, + a[y] 0 <= x, y < n
模板
template <typename T>
struct FenwickTree {
int n;
vector<T> a;
FenwickTree(int n) : n(n), a(n) {}
FenwickTree(vector<T> &A) : FenwickTree((int)A.size()) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) add(i, A[i]);
}
void add(int x, T v) {
for (int i = x + 1; i <= n; i += i & -i) a[i - 1] += v;
}
T ask(int x) {
T ans = 0;
for (int i = min(x + 1, n); i > 0; i -= i & -i) ans += a[i - 1];
return ans;
}
T ask(int l, int r) { //sum[l..r]
if (l > r) return 0;
return ask(r) - ask(l - 1);
}
};
二维树状数组
用法
- 初始化: FenwickTree2D
fen(n, m); 或者 FenwickTree2D fen(a); a 是二维vector - 添加元素: fen.add(i, j, val) 0 <= i < n, 0 <= j < m;
- 查询前缀和: fen.ask(x, y) 0 <= x < n, 0 <= y < m
- 查询区间和: fen.ask(x1, y1, x2, y2) sum[x1..x2, y1..y2] 0 <= x1, x2 < n, 0 <= y1, y2 < m
模版
template<typename T>
struct FenwickTree2D{
vector<vector<T>> tr;
int n, m;
FenwickTree2D(int N, int M) : n(N), m(M), tr(N, vector<T>(M, 0)){}
FenwickTree2D(vector<vector<T>> &a) : FenwickTree2D((int)a.size(), (int)a[0].size()) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j)
add(i, j, a[i][j]);
}
void add(int x, int y, T val){ // 0 <= x < n, 0 <= y < m
for(int i = x + 1; i <= n; i += i & -i)
for(int j = y + 1; j <= m; j += j & -j)
tr[i - 1][j - 1] += val;
}
T ask(int x, int y) { // 0 <= x < n, 0 <= y < m
T ret = 0;
for(int i = x + 1; i > 0; i -= i & -i)
for(int j = y + 1; j > 0; j -= j & -j)
ret += tr[i - 1][j - 1];
return ret;
}
T ask(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) { // sum[x1..x2, y1..y2]
return ask(x2, y2) - ask(x2, y1 - 1) - ask(x1 - 1, y2) + ask(x1 - 1, y1 - 1);
}
};
线段树
st表
ST表类似树状数组,线段树这两种算法,是一种用于解决RMQ(Range Minimum/Maximum Query,即区间最值查询)问题的离线算法
与线段树相比,预处理复杂度同为O(nlogn),查询时间上,ST表为O(1),线段树为 O(logn)
算法
ST表是利用的是倍增的思想
f[i][j]表示从i位起的2^j个数中的最大数,即[i,i+2^j-1]中的最大值,从其定义中可以看出来。
预处理
- f[i][0]表示[i,i]中的最大值,只能是a[i],故f[i][0]=a[i]。
- 对于任意的f[j][i],我们分成两段相等长度的数列来看,
[j,j+2^(i-1)-1]和[j+2^(i-1),j+2^i-1],分别对应f[j][i-1]和f[j+(1«i-1)][i-1]。既然这两段的最大值都知道了,它们又恰好完全地覆盖了[j,j+2^i-1],它俩的最大值就是这个区间的最大值。
查询
- 对于区间
[l,r],先确定一个长度2^k,其中k=log2(r-l+1)。这个长度2^k保证小于等于r-l+1,因为k是向下取整的。
- 以l为起始点,往右查询,即f[l][k];再以r为结束点,往左查询,即f[r-(1«k)+1][k]。
- 要理解
r-(1<<k)+1为什么要加1,把两者比较一下,其最大值就是[l,r]中的最大值.
预处理代码:
int a[1010] //原数组
int st[1010][20] // st[表]
void init(int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
st[i][0] = a[i];
for (int j = 1; (1 << j) <= n; ++j) {
for (int i = 0; i + (1 << j) - 1 < n; ++i) {
st[i][j] = max(st[i][j - 1], st[i + (1 << (j-1))][j - 1]);
}
}
}
查询代码:
int search(int l, int r) {
int k = log2(r - l + 1);
return max(f[l][k], f[r-(1<<k)+1][k]);
}
字典树trie
实现一个 Trie (前缀树),包含 insert, search, 和 startsWith 这三个操作。
- 你可以假设所有的输入都是由小写字母 a-z 构成的。
- 保证所有输入均为非空字符串。
示例
Trie trie = new Trie();
trie.insert("apple");
trie.search("apple"); // 返回 true
trie.search("app"); // 返回 false
trie.startsWith("app"); // 返回 true
trie.insert("app");
trie.search("app"); // 返回 true
class Trie {
bool is_str = false;
Trie * next[26] = {nullptr};
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
Trie() {}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
void insert(string w) {
Trie* node = this;
for(auto c : w) {
if (node->next[c - 'a'] == nullptr)
node->next[c - 'a'] = new Trie();
node = node->next[c - 'a'];
}
node->is_str = true;
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
bool search(string w) {
Trie* node = this;
for (auto c : w) {
if (node->next[c - 'a'] == nullptr)
return false;
node = node->next[c - 'a'];
}
return node->is_str;
}
/** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */
bool startsWith(string prefix) {
Trie* node = this;
for (auto c : prefix) {
if (node->next[c - 'a'] == nullptr)
return false;
node = node->next[c - 'a'];
}
return true;
}
};





